Ceci est une ancienne révision du document !
Table des matières
A. Configuration des interfaces des routeurs
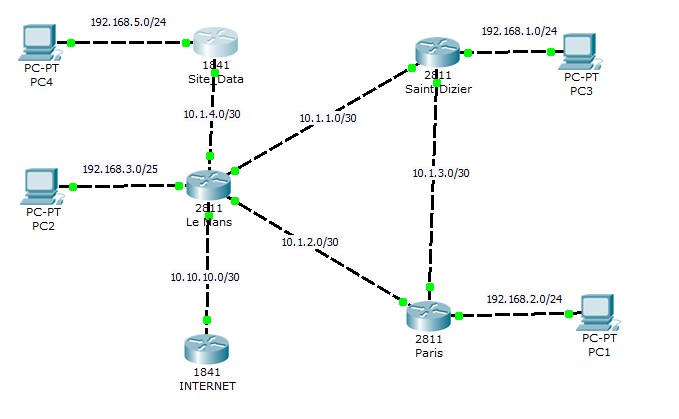
Commençons par attribuer les adresses IP sur les interfaces des routeurs, conformément au tableau ci-dessus, pour chacun des sites de l'architecture.
Le Mans :
Le Mans(config)#interface fastEthernet 0/0 -> on rentre dans le mode configuration d’interface Le Mans(config-if)#ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252 -> affectation d’une adresse ip Le Mans(config-if)#no sh -> passer l’interface up Le Mans(config-if)#exit Le Mans(config)#interface fastEthernet 0/1 Le Mans(config-if)#ip address 10.1.2.1 255.255.255.252 Le Mans(config-if)#no sh Le Mans(config-if)#exit Le Mans(config)#interface ethernet 1/0 Le Mans(config-if)#ip address 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.128 Le Mans(config-if)#no sh Le Mans(config-if)#exit Le Mans(config)#interface ethernet 0/0/0 Le Mans(config-if)#ip address 10.1.4.1 255.255.255.252 Le Mans(config-if)#no sh Le Mans(config-if)#exit Le Mans(config)#interface ethernet 0/1/0 Le Mans(config-if)#ip address 10.10.10.2 255.255.255.252 Le Mans(config-if)#no sh Le Mans(config-if)#exit
Paris :
Paris(config)#interface fastEthernet 0/0 Paris(config-if)#ip address 10.1.3.1 255.255.255.252 Paris(config-if)#no sh Paris(config-if)#exit Paris(config)#interface fastEthernet 0/1 Paris(config-if)#ip address 10.1.2.2 255.255.255.252 Paris(config-if)#no sh Paris(config-if)#exit Paris(config)#interface ethernet 1/0 Paris(config-if)#ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 Paris(config-if)#no sh Paris(config-if)#exit
Saint-Dizier :
Saint-Dizier(config)#interface fastEthernet 0/0 Saint-Dizier(config-if)#ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.252 Saint-Dizier(config-if)#no sh Saint-Dizier(config-if)#exit Saint-Dizier(config)#interface fastEthernet 0/1 Saint-Dizier(config-if)#ip address 10.1.3.2 255.255.255.252 Saint-Dizier(config-if)#no sh Saint-Dizier(config-if)#exit Saint-Dizier(config)#interface Ethernet 1/0 Saint-Dizier(config-if)#ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 Saint-Dizier(config-if)#no sh Saint-Dizier(config-if)#exit
Internet :
INTERNET(config)#interface fastEthernet 0/0 INTERNET(config-if)#ip address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.252 INTERNET(config-if)#no sh INTERNET(config-if)#exit
Site_Data :
Site_Data(config)#interface fastEthernet 0/1 Site_Data(config-if)#ip address 10.1.4.2 255.255.255.252 Site_Data(config-if)#no sh Site_Data(config-if)#exit Site_Data(config)#interface fastEthernet 0/0 Site_Data(config-if)#ip address 192.168.5.1 255.255.255.0 Site_Data(config-if)#no sh Site_Data(config-if)#exit
A cette étape vous devez pouvoir faire :
Chaque PC ping sa passerelle Chaque routeur ping les autres routeurs du même sous réseau
Maintenant il faut que les PC des différents sous réseaux puissent communiquer entre eux.
B. Mise en place du protocole de routage RIP version 2
Le Mans :
Le Mans(config)#router rip -> activation du processus RIP Le Mans(config-router)#version 2 -> utilisation de la version 2 de RIP Le Mans(config-router)#no auto-summary -> désactivation de l’agrégation de routes Le Mans(config-router)#network 192.168.3.0 -> déclaration d’un réseau Le Mans(config-router)#network 10.1.1.0 Le Mans(config-router)#network 10.1.2.0 Le Mans(config-router)#exit Le Mans#debug ip rip -> permet de voir le debug du protocole RIP (utile en cas incident ou de mauvaise manipulation)
Paris :
Paris(config)#router rip Paris(config-router)#version 2 Paris(config-router)#no auto-summary Paris(config-router)#network 10.1.3.0 Paris(config-router)#network 10.1.2.0 Paris(config-router)#network 192.168.2.0 Paris(config-router)#exit
Saint-Dizier :
Saint-Dizier(config)#router rip Saint-Dizier(config-router)#version 2 Saint-Dizier(config-router)#no auto-summary Saint-Dizier(config-router)#network 10.1.1.0 Saint-Dizier(config-router)#network 10.1.3.0 Saint-Dizier(config-router)#network 192.168.1.0 Saint-Dizier(config-router)#exit Saint-Dizier(config)#exit
A cette étape les réseaux de Paris, Le Mans et Saint-Dizier sont joignables entre eux, vous devez avoir les tables de routage suivantes :
Le Mans :
Le Mans#show ip route -> visualiser la table de routage Codes: C - connected, S - static, I - IGRP, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2 E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP i - IS-IS, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2, ia - IS-IS inter area * - candidate default, U - per-user static route, o - ODR P - periodic downloaded static route Gateway of last resort is not set 10.0.0.0/30 is subnetted, 3 subnets C 10.1.1.0 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0 C 10.1.2.0 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/1 R 10.1.3.0 [120/1] via 10.1.2.2, 00:00:08, FastEthernet0/1 [120/1] via 10.1.1.2, 00:00:22, FastEthernet0/0 R 192.168.1.0/24 [120/1] via 10.1.1.2, 00:00:22, FastEthernet0/0 R 192.168.2.0/24 [120/1] via 10.1.2.2, 00:00:08, FastEthernet0/1 192.168.3.0/25 is subnetted, 1 subnets C 192.168.3.0 is directly connected, Ethernet1/0
Dans une table de route comme ci-dessus, vous verrez que la lettre au début de chaque ligne de routage indique le type de route, par exemple lorsqu'un “R” est indiqué c'est qu'il s'agit d'une route générée à partir du protocole RIP.
Paris :
Paris#show ip route 10.0.0.0/30 is subnetted, 3 subnets R 10.1.1.0 [120/1] via 10.1.2.1, 00:00:05, FastEthernet0/1 [120/1] via 10.1.3.2, 00:00:09, FastEthernet0/0 C 10.1.2.0 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/1 C 10.1.3.0 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0 R 192.168.1.0/24 [120/1] via 10.1.3.2, 00:00:09, FastEthernet0/0 C 192.168.2.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet1/0 192.168.3.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks R 192.168.3.0/24 [120/10] via 10.1.2.1, 00:00:05, FastEthernet0/1 R 192.168.3.0/25 [120/1] via 10.1.2.1, 00:00:05, FastEthernet0/1
Saint-Dizier :
Saint-Dizier#show ip route 10.0.0.0/30 is subnetted, 3 subnets C 10.1.1.0 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0 R 10.1.2.0 [120/1] via 10.1.3.1, 00:00:14, FastEthernet0/1 [120/1] via 10.1.1.1, 00:00:15, FastEthernet0/0 C 10.1.3.0 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/1 C 192.168.1.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet1/0 R 192.168.2.0/24 [120/1] via 10.1.3.1, 00:00:14, FastEthernet0/1 192.168.3.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks R 192.168.3.0/24 [120/14] via 10.1.3.1, 00:00:14, FastEthernet0/1 R 192.168.3.0/25 [120/1] via 10.1.1.1, 00:00:15, FastEthernet0/0
Maintenant, nous allons réaliser la mise en place d’une route statique sur le site du Mans vers le Site_Data puis diffusion de la route statique à travers le protocole RIP.
Le Mans(config)#ip route 192.168.5.0 255.255.255.0 10.1.4.2 -> mise en place d’une route statique Le Mans(config)#router rip -> activation du protocole rip Le Mans(config-router)#redistribute static -> on redistribue la route statique via RIP
A cette étape la route statique est diffusée entre les routeurs participants au routage dynamique RIP :
Paris#show ip route 10.0.0.0/30 is subnetted, 5 subnets R 10.1.1.0 [120/1] via 10.1.2.1, 00:00:06, FastEthernet0/1 [120/1] via 10.1.3.2, 00:00:03, FastEthernet0/0 C 10.1.2.0 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/1 C 10.1.3.0 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0 R 10.1.4.0 [120/1] via 10.1.2.1, 00:00:06, FastEthernet0/1 R 10.10.10.0 [120/1] via 10.1.2.1, 00:00:06, FastEthernet0/1 R 192.168.1.0/24 [120/1] via 10.1.3.2, 00:00:03, FastEthernet0/0 C 192.168.2.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet1/0 192.168.3.0/25 is subnetted, 1 subnets R 192.168.3.0 [120/1] via 10.1.2.1, 00:00:06, FastEthernet0/1 R 192.168.5.0/24 [120/1] via 10.1.2.1, 00:00:25, FastEthernet0/1
Mais à ce stade le réseau 192.168.5.0/24 est injoignable depuis Paris et Saint-Dizier.
La raison est simple le routeur Site_Data ne connais pas les routes vers les réseaux de Paris et Saint-Dizier :
Site_Data#show ip route 10.0.0.0/30 is subnetted, 1 subnets C 10.1.4.0 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/1 C 192.168.5.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
Afin de résoudre, ce problème pour une question pratique nous allons mettre en place une passerelle par défaut sur le routeur Site_Data :
Site_Data(config)#ip default-network 10.1.4.1 -> mise en place d’une passerelle par défaut
Depuis les routeurs de Paris et Saint-Dizier :
Paris#ping 192.168.5.10 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.5.10, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 10/14/18 ms
Puis :
Saint-Dizier#ping 192.168.5.10 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.5.10, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 11/15/19 ms
Mettons en place une gateway pour accéder à internet à partir du site du Mans, que nous allons propager aux sites de Paris et Saint-Dizier via le protocole RIP :
Le Mans(config)#ip default-network 10.10.10.1 -> mise en place d’une passerelle par défaut Le Mans(config)#router rip -> on rentre dans le processus rip Le Mans(config-router)#default-information originate -> diffusion de la route par défaut dans rip.
Vérification de la table de routage sur le routeur de Saint-Dizier :
Saint-Dizier#show ip route
10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 6 subnets, 2 masks R 10.0.0.0/8 [120/1] via 10.1.1.1, 00:03:28, FastEthernet0/0 [120/1] via 10.1.3.1, 00:00:18, FastEthernet0/1 C 10.1.1.0/30 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0 R 10.1.2.0/30 [120/1] via 10.1.1.1, 00:00:27, FastEthernet0/0 [120/1] via 10.1.3.1, 00:00:18, FastEthernet0/1 C 10.1.3.0/30 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/1 R 10.1.4.0/30 [120/1] via 10.1.1.1, 00:00:27, FastEthernet0/0 R 10.10.10.0/30 [120/1] via 10.1.1.1, 00:00:27, FastEthernet0/0 C 192.168.1.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet1/0 R 192.168.2.0/24 [120/1] via 10.1.3.1, 00:00:18, FastEthernet0/1 192.168.3.0/25 is subnetted, 1 subnets R 192.168.3.0 [120/1] via 10.1.1.1, 00:00:27, FastEthernet0/0 R 192.168.5.0/24 [120/1] via 10.1.1.1, 00:23:49, FastEthernet0/0 [120/1] via 10.1.3.1, 00:00:18, FastEthernet0/1 R* 0.0.0.0/0 [120/1] via 10.1.1.1, 00:00:27, FastEthernet0/0
C. Mise à jour de RIP : Utilisation de la commande passive interface
Le protocole RIP envoi la mise à jour sur toutes les interfaces des routeurs par défaut, ce qui génère du trafic réseau.
Nous allons limiter les MAJ RIP aux interfaces d’interconnexion entre les routeurs du Mans, Paris et Saint-Dizier.
Le Mans :
Le Mans(config-router)#router rip -> on rentre dans le processus RIP Le Mans(config-router)#passive-interface ethernet 1/0 -> on désactive l’envoi de MAJ RIP sur une interface du routeur Le Mans(config-router)#passive-interface ethernet 0/0/0 Le Mans(config-router)#passive-interface ethernet 0/1/0
Voilà, c'est fait pour Le Mans, nous allons réaliser la même opération pour Paris et Saint-Dizier.
Paris :
Paris(config)#router rip Paris(config-router)#passive-interface ethernet 1/0
Saint-Dizier :
Saint-Dizier(config)#router rip Saint-Dizier(config-router)#passive-interface ethernet 1/0
En mode enable vous pouvez vérifier en temps réel que les MAJ RIP ne passent plus par les interfaces spécifiées, par la commande : debug ip rip.
Pour enlever le mode debug en enable vous faites : no debug ip rip
Sinon vous pouvez utiliser la commande : show ip protocols
Exemple :
Paris#show ip protocols Routing Protocol is "rip" Sending updates every 30 seconds, next due in 21 seconds Invalid after 180 seconds, hold down 180, flushed after 240 Outgoing update filter list for all interfaces is not set Incoming update filter list for all interfaces is not set Redistributing: rip Default version control: send version 2, receive 2 Interface Send Recv Triggered RIP Key-chain FastEthernet0/0 2 2 FastEthernet0/1 2 2 Automatic network summarization is not in effect Maximum path: 4 Routing for Networks: 10.0.0.0 192.168.2.0 Passive Interface(s): Ethernet1/0 Routing Information Sources: Gateway Distance Last Update 10.1.2.1 120 00:00:23 10.1.3.2 120 00:00:00 Distance: (default is 120)